What Is Industrial IoT? A Simple Guide
In a world where technology evolves at a breakneck speed, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) emerges as a beacon of transformation, reshaping the landscape of manufacturing and industrial processes. Imagine a symphony of smart devices harmonizing to optimize production, improve efficiency, and elevate business outcomes. Welcome to the dawn of a new era—an era where the line between the physical and digital blurs, unlocking unprecedented potential. In this guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of IIoT, exploring its essence, its impact, and the innovations it heralds.
Understanding the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) often conjures images of smart homes and interconnected gadgets that simplify our daily lives. However, when we shift our gaze to the industrial sector, IoT takes on a new identity—hence, the term Industrial IoT or IIoT.
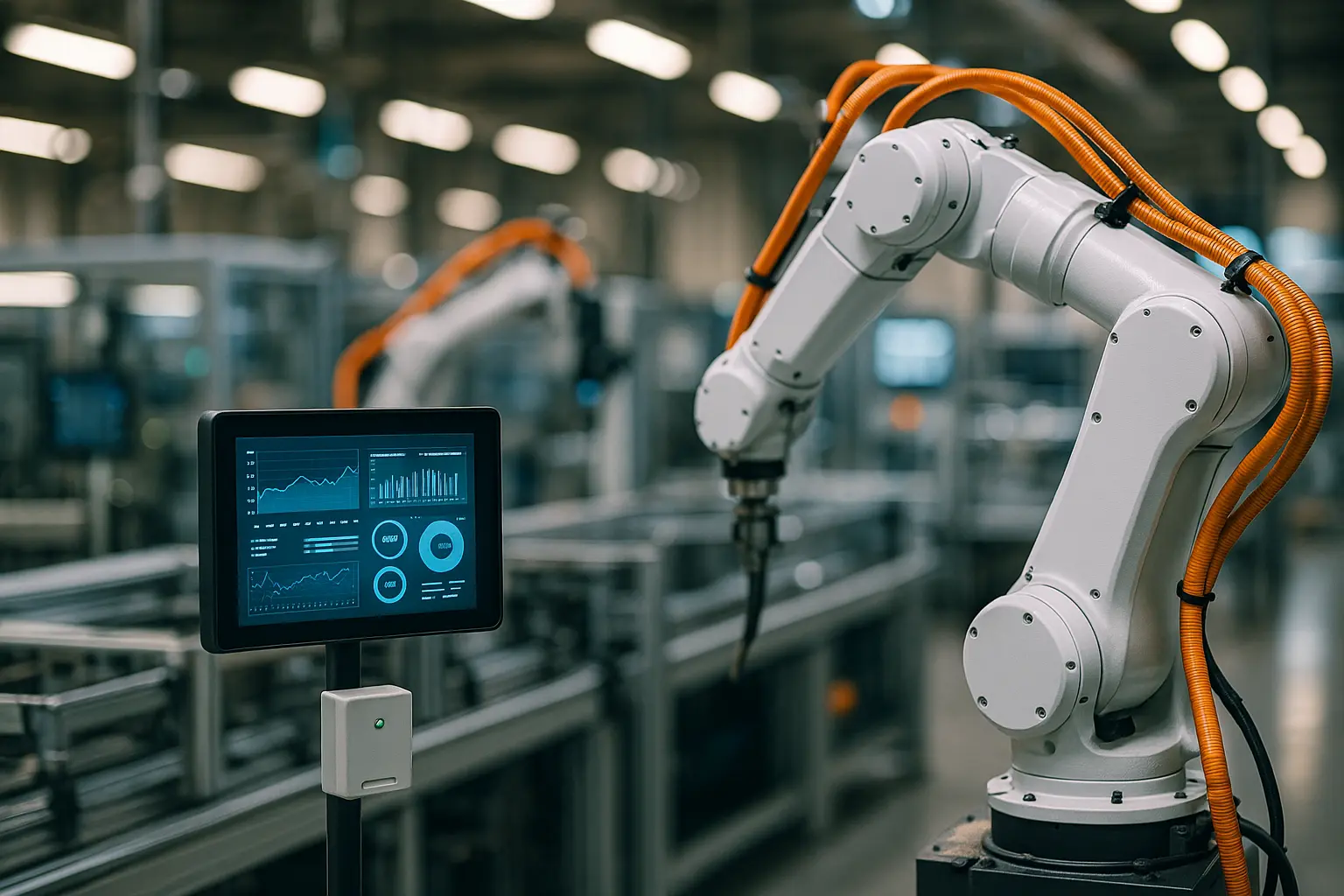
IIoT is a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems, seamlessly communicating within industrial settings to optimize processes and operations. It transcends the confines of personal use, infiltrating factories, assembly lines, and supply chains, rendering them smarter and more efficient.
In the industrial realm, IIoT stands as a robust framework where data becomes the nucleus of operations. Real-time data curation and analysis allow businesses to make informed decisions, anticipate potential issues, and manage resources efficiently. Imagine a manufacturing unit where sensors continuously monitor equipment health, alerting teams to maintenance needs before an issue escalates. This kind of predictive maintenance is a hallmark of IIoT, mitigating downtime and enhancing productivity.
The key players in IIoT include sensors, actuators, and connectivity frameworks, all working in synergy to gather data and execute on-demand actions. The crux lies in analyzing this data via advanced analytics or machine learning algorithms to yield actionable insights. It’s not just about collecting data—it’s about harnessing it to drive tangible outcomes.
As we delve deeper, we unravel the myriad ways IIoT reshapes industries, heralding a new age of industrial innovation.
Key Applications of IIoT in Modern Industry
From agriculture to aerospace, IIoT’s footprint is vast and varied, breathing life into industries traditionally considered rigid and inflexible. Its applications are as diverse as they are impactful, illustrating the sheer versatility of this technology.
Smart Manufacturing: Modern manufacturing plants are a hub of innovation, with IIoT at their core. By integrating smart systems, manufacturers can streamline their operations, reducing waste and optimizing resource use. Real-time data from the production floor allows us to identify bottlenecks, predict equipment failures, and ensure that production lines run smoothly.
Supply Chain Optimization: In an era of globalization, supply chains span continents, making their management increasingly complex. IIoT provides unparalleled visibility, allowing companies to track shipments in real-time, monitor storage conditions, and forecast demand accurately. Such insights empower businesses to respond swiftly to changes, ensuring that customers receive their products promptly.
Energy Management: For industries reliant on extensive energy use, IIoT offers solutions that enhance sustainability. By monitoring energy consumption patterns, businesses can identify inefficiencies and implement measures to reduce their carbon footprint. The integration of smart grids and IoT-enabled meters facilitates real-time adjustments, optimizing energy use dynamically.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: In sectors where precision is paramount, IIoT ensures quality and compliance. Smart sensors monitor environmental conditions within pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, ensuring that products meet stringent standards. In hospitals, connected devices help in patient monitoring, delivering timely interventions and improving care quality.
By tailoring these technologies to specific industry needs, IIoT fosters a culture of continuous improvement and resilience, paving the way for future innovations.
Benefits and Challenges of Adopting IIoT
As industries pivot towards IIoT adoption, the promise of numerous benefits serves as a catalyst for change. Yet, this transformation is not without its challenges, requiring strategic foresight and meticulous planning.
Benefits of IIoT Adoption:
- Efficiency and Productivity: With real-time data insights, businesses can optimize processes, reducing waste and increasing throughput. Smart sensors detect anomalies and fine-tune operations, ensuring resources are used judiciously.
- Cost Reduction: Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtimes, cutting repair costs and extending equipment lifespan. By avoiding unnecessary energy use, companies can also make significant savings.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Instantaneous data collection and analysis empower businesses to make informed decisions, whether related to inventory management or production schedules.
- Safety and Compliance: Connected devices continuously monitor workplace conditions, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and minimizing risks.
Challenges to Overcome:
- Data Security: With increased connectivity comes heightened vulnerability. Safeguarding sensitive information and protecting networks from cyber threats remain a priority.
- Integration Complexities: Aligning existing infrastructure with IIoT solutions requires careful planning and execution. Interoperability between devices and systems is crucial for seamless operation.
- Scalability Issues: Growing IIoT networks require robust frameworks to manage increased data flow and device connectivity.
- Skill Gaps: As IIoT intricacies deepen, the demand for skilled professionals rises, necessitating investments in training and development.
While the transition to IIoT is a formidable task, the advantages it offers far outweigh the challenges. By addressing these hurdles, industries can unlock unparalleled growth and innovation.
The Future of IIoT: A Look Ahead
Standing at the crossroads of technology and industry, we find ourselves on the brink of a revolution spurred by IIoT. As technological advancements accelerate, the potential applications and implications of IIoT expand, painting an exciting canvas for the future.
Emerging Trends:
- Edge Computing: As data volume grows, processing it closer to the source becomes imperative. Edge computing complements IIoT by enabling real-time analytics and reducing latency, enhancing decision-making speed and accuracy.
- AI Integration: The synergy between AI and IIoT drives innovations in automation and machine learning. By integrating AI, IIoT systems can learn, adapt, and optimize processes autonomously, marking a leap towards self-sustaining ecosystems.
- Blockchain for Security: As industries become increasingly digitized, safeguarding data integrity is crucial. Blockchain technologies offer secure, transparent solutions to address security concerns inherent in IIoT ecosystems.
- Sustainability Initiatives: With a growing emphasis on environmental responsibility, industries leverage IIoT to reduce waste and promote sustainable practices. From intelligent energy management to resource optimization, IIoT plays a pivotal role in shaping a greener future.
The journey ahead is both exhilarating and challenging, with IIoT poised to redefine the industrial landscape. As we embrace these opportunities, we must remain vigilant, adapting to the demands of this ever-evolving domain. The future of IIoT holds promise, beckoning us to explore, innovate, and redefine the boundaries of possibility.
As we stand on the precipice of an IIoT-driven future, it is evident that the fusion of technology and industry holds transformative power. The Industrial Internet of Things embodies the pivotal shift towards smarter, more efficient processes that redefine the way we view manufacturing, management, and maintenance. From optimizing supply chains to enhancing safety standards, IIoT offers a blueprint for sustainable growth and innovation.
In this ever-evolving landscape, our collective foresight, adaptability, and readiness to embrace change will determine the success of IIoT integration. As businesses and industries worldwide harness the potential of interconnected devices, we unlock doors to new possibilities, propelling us towards a future marked by efficiency, sustainability, and progress. The IIoT revolution is not merely a trend—it’s a transformative journey that beckons us to explore the infinite realms of innovation and redefine the art of the possible.
FAQ
What exactly does Industrial IoT (IIoT) mean?
Industrial IoT, or IIoT, refers to the integration of smart sensors and devices into industrial operations, allowing for real-time data collection, exchange, and analysis to enhance productivity and efficiency in various sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and energy.
How does Industrial IoT differ from regular IoT?
While both involve connected devices, Industrial IoT focuses on applications in industrial sectors, emphasizing heavy machinery, manufacturing, and infrastructure, whereas regular IoT includes a broader range of consumer and commercial applications, such as smart homes and wearable technology.
What are the key benefits of implementing Industrial IoT?
Implementing Industrial IoT can lead to increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, improved safety, predictive maintenance, and better decision-making through comprehensive data analysis and insights.
What kinds of technologies are involved in Industrial IoT?
Technologies integral to IIoT include sensors, machine-to-machine communication, cloud computing, advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity measures to ensure data protection and integrity.
What are some common challenges faced when adopting Industrial IoT?
Challenges include ensuring data security, managing the complexity of integrating legacy systems with new technologies, high initial implementation costs, and the need for skilled personnel to manage and analyze the vast amounts of data generated.













